

Gray matter is somewhat denser on CT than white matter. The gray matter is at the outside of the brain parenchyma. In brain edema, the sulci will be compressed, as opposed to atrophy (as in Alzheimers disease) here the sulci will expand as a result of tissue loss. Santosh Chandrasekaran, co-lead author of the study, said this process has allowed researchers to deepen their knowledge of neural circuitry in processing touch-related sensations in the human brain. The brain surface consists of gyri (ridges) and sulci (grooves). These gyri and sulci form important landmarks that allow us to separate the brain into functional centers.
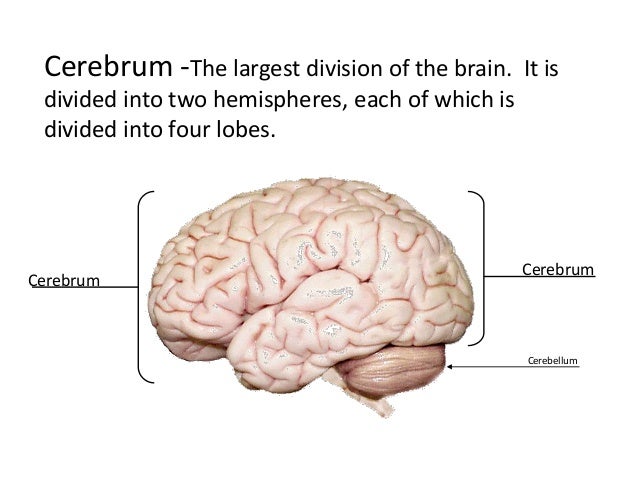
The new research is particularly important as it shows that stimulation of harder-to-reach areas of the brain can evoke precise sensory precepts in the fingertips. The surface of the brain, known as the cerebral cortex, is very uneven, characterized by a distinctive pattern of folds or bumps, known as gyri (singular: gyrus), and grooves, known as sulci (singular: sulcus). Previously, researchers have been able to electrically stimulate certain areas of the brain and restore some sensation to the hand. To understand the response of the brain, the same electrodes were used to record neural signals as well. When electrical stimulation was provided to the patients, they reported a sort of tingling in the hand and fingertips. The research was published in the Brain Stimulation journal.Ī team led by Ashesh Mehta, neurosurgeon and co-principal investigator on the study, implanted two patients with the stereoelectroencephalography (SEEG) electrodes in the sulci (grooves) of the brain. The research report states that the procedure to implant the electrode is minimally invasive. There could be many other reasons for a person to lose the sense of touch – like stroke, diabetes, or spinal cord injury. superior temporal gyrus Sulci slf II slfIII sstr tp ilf acs calcarine sulcus, anterior part cos collateral sulcus ils intralingual sulcus impI anterior. Imagine a person not being able to feel the touch of another person. The condition also creates difficulty in everyday movements and takes an emotional toll on people. Their path-breaking research can potentially help millions of people who live with paralysis and neuropathy (nerve damage). Scientists from the Feinstein Institutes for Medical Research said the procedure requires an electrode implant in the brain. The cerebrum is divided into the left and right hemispheres by a deep longitudinal fissure the two hemispheres remain in contact and communication with one. The cerebrum controls somatosensory, motor, language, cognitive thought, memory, emotions, hearing, and vision. Taking up the majority of the brain space is the cerebrum. Researchers at a New York-based institute said they have found a way to restore the sense of touch in a person who may have lost it due to an illness or injury. The brain consists of the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
